Assessment Of The Improved Reoencephalography Method For Evaluating Brain Blood Flow
Having an instrumentation that allows the continuous assessment of cerebral blood flow in patients with cerebrovascular pathologies would be of vital importance in clinical practice.
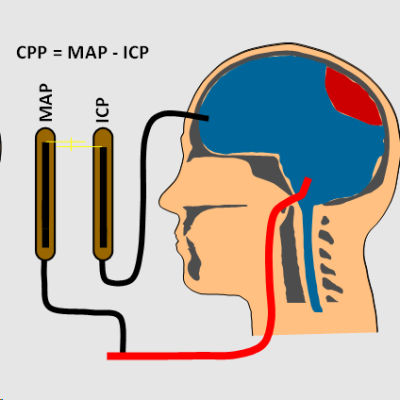
The so-called reoencephalography, also named transcranial impedance plethysmography, emerged in the fifties to cover this goal, but its study was abandoned after twenty-five years of intense debate about its measurement capacity. Recent studies carried out by our research group have allowed deciphering the information contained in the reoencephalographic record and extracting information about cerebral blood flow from it.
The electromedical equipment required for this, called “Improved Reoencephalograph”, is currently under a patent claim.
Although the results obtained in preliminary trials suggest the authenticity of the measure, it is necessary to contrast the Enhanced Reoencephalography with other standard measurement techniques in order to disseminate the results and extend the studies to the clinical setting.
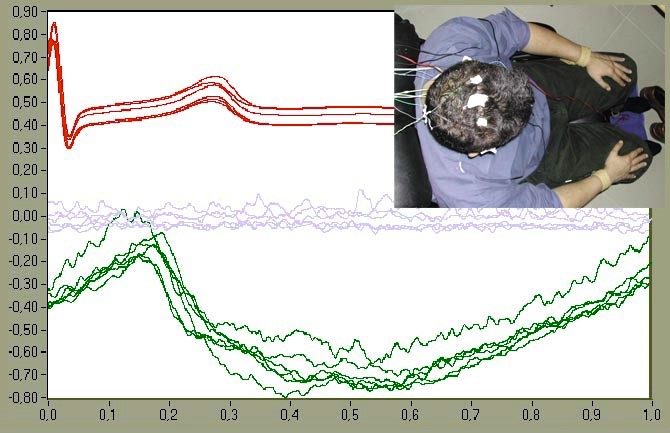
This project contrasts the registry provided by a system of Enhanced Reoencephalography with that obtained by transcranial Doppler in voluntary subjects in two different physiological conditions: psychophysical rest and cerebral vasodilation. In turn, it verifies that the signal provided by Enhanced Reoencephalography is not contaminated by the main source of interference of classical reoencephalography: the blood pulsatility of the scalp.
In this way, Enhanced Reoencephalography would allow the continuous assessment of cerebral blood flow by a non-invasive, portable, low cost instrumentation, without side effects and easy to use.
1. Development of a REG-M semiautomatic system, with a double channel REG-II and a single channel REG-I
2. Evaluation of the REG M method as indirect technique for VSC variations associated to the heartbeat.
Publications
- Juan J Perez; Enrique Guijarro; Jeronimo Sancho. Spatiotemporal pattern of the extracranial component of the reoencephalographic signal. PHYSIOLOGICAL MEASUREMENT. 26, pp. 925 – 938. 2005. ISSN 0967-3334
- Juan J. Perez; Enrique Guijarro; Pedro Ortiz; José M. Pons. Enhanced Rheoencephalography. Encyclopedia of healthcare information systems. 1, pp. 519 – 526. Information Science Reference (IGI Global), 2008. ISSN 978-1- 59904-889- 5
- Juan J. Perez; Enrique Guijarro; Pedro Ortiz; José M. Pons. New Perspectives in Rheoencephalography. Encyclopedia of healthcare information systems. 2, pp. 990 – 997. Information Science Reference (IGI Global), 2008. ISSN 978-1- 59904-889- 5
Patent
Title: “A device and method for obtaining information related to cerebral haemodynamics”.
Inventors: Pérez Juan J; Guijarro Estelles Enrique
Assignee: UNIVERSIDAD POLITECNICA DE VALENCIA
Patent number: P200502417